Submitted by Jon Reed on
5G refers to the fifth generation of cellular network technology that will eventually replace 4G, which is what most smartphones use today. Data transfer rates are many times faster on 5G, with the potential to be many, many times faster, so much so that it could possibly replace your home cable internet at some point. While 4G LTE supports peak download speeds of around 300 megabits per second (Mbps), average download speeds vary by carrier and are generally under 100 Mbps. 5G has reached 1.8 gigabits per second, with a theoretical potential max speed of 20 Gbps, which would let you download a feature length high definition movie in a few seconds.
5G technology operates on three bands - low-band, which offers speeds slightly higher than 4G over a similar range; mid-band, which currently supports speeds up to 900 Mbps and uses cell towers that cover a radius of several miles; high-band, which achieves the fastest speeds but only over short distances. The high-band range uses millimeter waves (mmWave) that require a completely different infrastructure than we are used to, employing short-range, low-powered nodes known as small cells. In the beginning, at least, high-band will likely only be deployed in densely populated areas and inside crowded structures like arenas, stadiums, concert venues, malls and the like.
Having three bands complicates understanding coverage. Whereas with 4G you could plainly see if your area is covered or not, with 5G you could have a carrier that is beefing up it's mid-band infrastructure but ignoring its low- and high-band, or you could be limited by a phone that works on low- and mid-band but doesn't support mmWave. There are currently only a handful of 5G phones on the market, mostly from Samsung, OnePlus and LG, but expect many more to appear before the year is out, including Apple's iPhone 12.
If you are looking forward to 5G service, you'll want to know what coverage your current carrier offers. While the major carriers all began deploying 5G in 2019, there is still a long way to go, and if it your carrier isn't covering your area, maybe it's time to switch. Here's where to check 5G coverage offered by the major carriers:Verizon
Newest iPhone FAQs
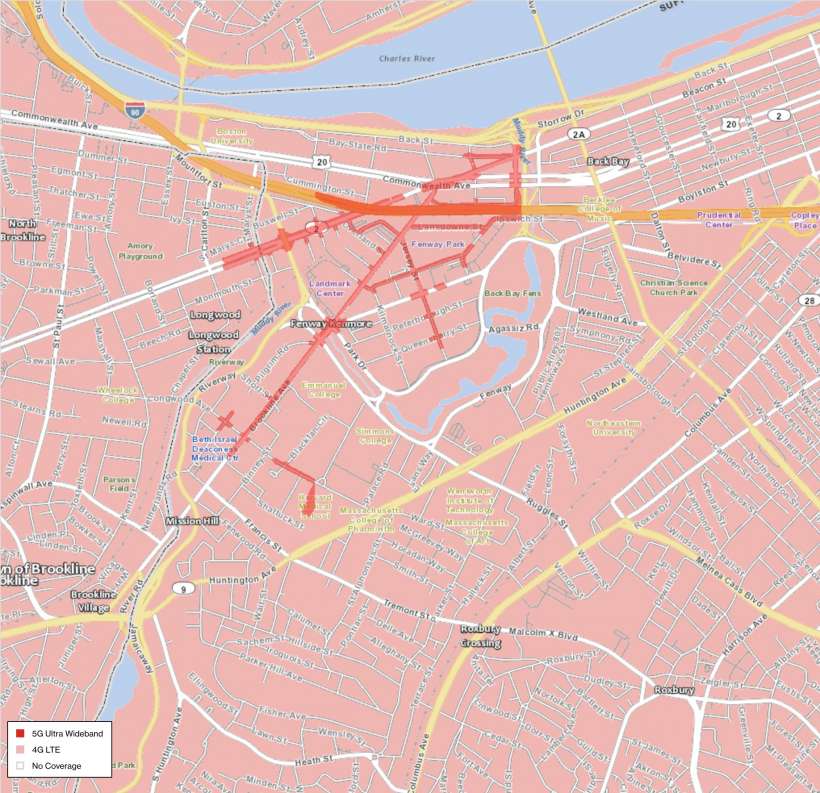
While Verizon claims that it has the fastest 5G, it also may have some of the worst coverage so far. The company is seemingly focused on deploying the high-band 5G network and therefore has only deployed in select cities. There is no national coverage map but you can see a list of cities (with maps) here.
AT&T
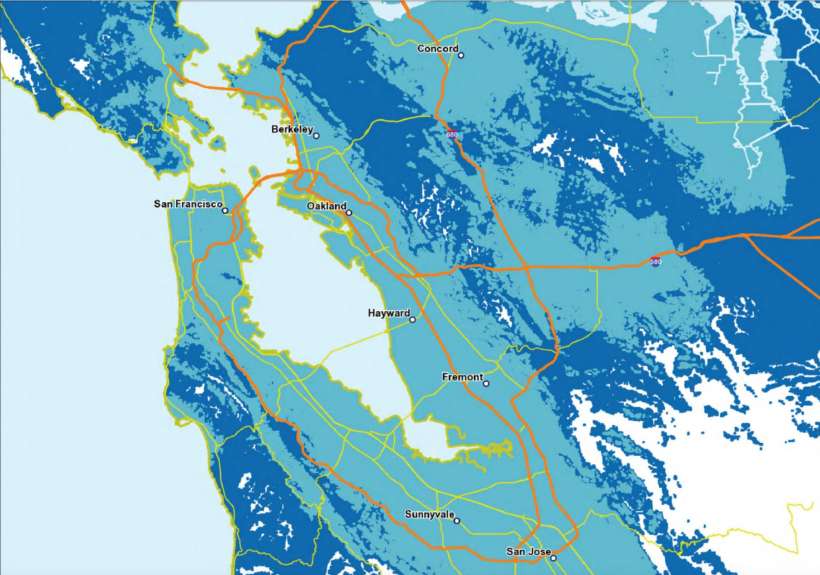
AT&T has been marketing 5G E (Evolution) for a while now, which is misleading since it is really just a faster version of 4G. That said, it looks like the company is expanding true 5G network's low- and mid-band coverage around the country and, like Verizon, expanding the high-band millimeter wave (which it is calling its 5G+ network) coverage in select cities. You can read about AT&T's 5G network and see individual state maps and a list of 5G+ cities here. You can also see a more detailed coverage map here.
T-Mobile/Sprint
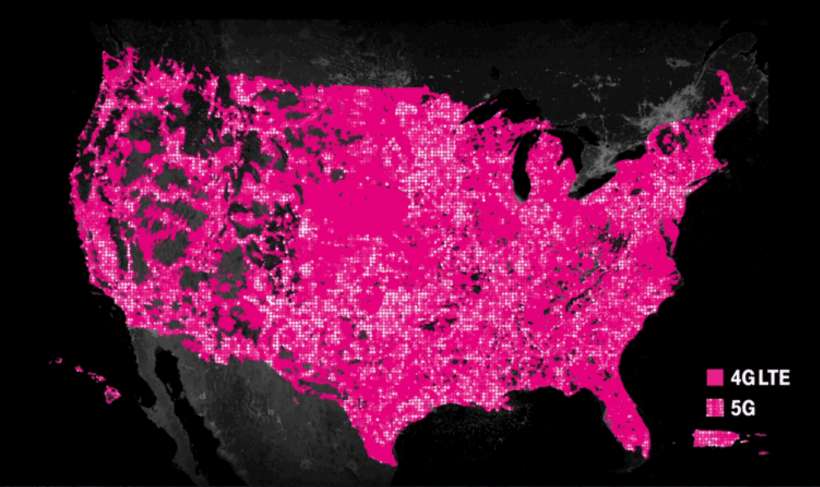
T-Mobile offers by far the most 5G coverage, but if you look at the fine print, it says that its coverage map shows 600 MHz coverage, which is low-band and only slightly faster than 4G LTE. On its 5G network info page the company says that its 5G network will be 8x faster than the current 4G LTE network in the first few years, and within six years it will be 15x faster and available to 99% of Americans.